When we talk about the ancient history of the world, many ancient texts and books covered the Different types, manners, and procedures of human problems to be treated successfully. But from all of them, the Indian methods and books like Sushrut Sahimta, Charak Samhita, Ayurveda, and Thirukkural are known as one of the most trusted ancient books to rely on human health, body positions, defending ourselves, and treatment of any diseases.
The sitting position is one of those elements that can help our health or can make it worse if we donŌĆÖt consider it worthy of being notified by the general public. This is why, you must make yourself aware of these sitting positions. If you are also looking to benefit yourselves by knowing all the different types of sitting positions, then read our blog to the end.
So, letŌĆÖs start-
What are the Sitting Positions?
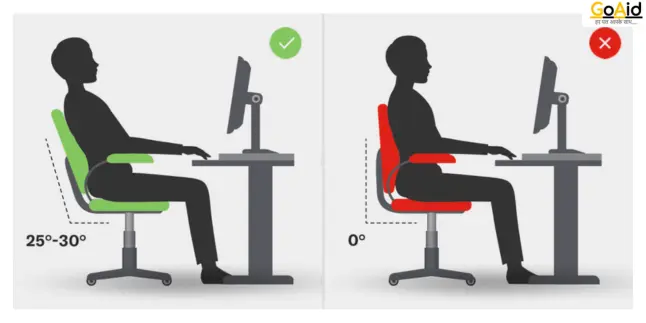
A sitting position refers to the posture and alignment of your body when you are seated. It involves how you position your spine, shoulders, hips, and legs to ensure comfort and reduce strain. Proper sitting positions can help prevent discomfort and health issues related to prolonged sitting, such as back pain, poor circulation, and muscle stiffness.
It’s important to maintain a balanced posture with your feet flat on the floor, your back straight, and your weight evenly distributed. Adopting good sitting positions can enhance your overall well-being, productivity, and energy levels throughout the day.
Read More: Introduction to Hospital Department List
What are Different Types of Sitting Positions? ŌĆō List of Sitting Positions Types
These are the top 15 types of Sitting Positions you should know about:
| SN | Sitting Position Names | Ancient Names / Simple Names | Description of Sitting Position |
| 1 | Cross-Legged | Sukhasana | Sitting with legs crossed over each other at the ankles or knees is often used for meditation. |
| 2 | Lotus Position | Padmasana | Sitting with each foot placed on the opposite thigh is typically used in yoga and meditation. |
| 3 | Kneeling | Vajrasana | Sitting back on your heels with knees bent and shins on the floor, is often seen in traditional Japanese settings. |
| 4 | Seiza | Seiza | A variation of kneeling where you sit back on your heels with the tops of your feet flat on the floor, is common in Japanese culture. |
| 5 | Chair Sitting | Kursi Pe Baithna | Sitting on a chair with your back straight, feet flat on the floor, and knees at a 90-degree angle. |
| 6 | Reclining | Aram Se Baithna | Sitting with your back leaned back at an angle, supported by a chair or sofa, often with legs extended. |
| 7 | Squatting | Malasana | Sitting with knees bent and heels close to the buttocks, with feet flat on the ground, is common in many cultures for eating or resting. |
| 8 | Side Sitting | Ek Or Se Baithna | Sitting with legs bent to one side, often with weight supported on one hip and one hand on the floor. |
| 9 | Butterfly Position | Baddha Konasana | Sitting with the soles of the feet together and knees bent outward, is often used for stretching. |
| 10 | Straddle Position | Upavistha Konasana | Sitting with legs spread wide apart and back straight, is often used in exercises or stretches. |
| 11 | Tailor Sitting | Baddha Virasana | Similar to cross-legged but with knees bent and feet tucked under the thighs, often used in casual settings. |
| 12 | Forward Bend | Paschimottanasana | Sitting with legs extended and bending forward from the hips is often used in stretching or yoga. |
| 13 | W-Sitting | W Baithna | Sitting with knees bent and legs splayed out to the sides, forming a W shape with the legs, common among children. |
| 14 | Side Straddle | Parsva Upavistha Konasana | Sitting with one leg extended to the side and the other bent is often used in yoga and stretching exercises. |
| 15 | Perching | Kinare Par Baithna | Sitting on the edge of a chair with thighs at a downward angle is often used to maintain a semi-standing posture. |
Full Details about All Major Types of Sitting Positions
This is the detailed information about the above listed Sitting Positions:
1. Sitting Position – Sukhasana

Sukhasana, or the cross-legged position, involves sitting with legs crossed over each other at the ankles or knees. This position keeps the spine erect, shoulders relaxed, and hands resting on the knees. It is often used in meditation and for promoting a calm and relaxed state.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Sukhasana is ideal for meditation, pranayama (breathing exercises), and light stretching. It is suitable for those looking to relax or engage in mindfulness practices. It is also a comfortable sitting position for informal gatherings or conversations on the floor.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Enhances flexibility in the hips and knees.
- Promotes an upright spine and good posture.
- Calms the mind and reduces stress, making it ideal for meditation.
- Improves focus and concentration.
- Can aid in digestion by promoting a relaxed abdomen.
2. Sitting Position – Padmasana

Padmasana, or the lotus position, involves sitting with each foot placed on the opposite thigh, forming a cross with the legs. This position ensures an erect spine and promotes physical stability. It is commonly used in yoga and meditation practices for its grounding and calming effects.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Padmasana is ideal for advanced meditation, deep breathing exercises, and certain yoga practices. It is recommended for those who have flexibility in their hips and knees. This position helps deepen concentration and is often used for prolonged sitting in meditation.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Promotes mental clarity and emotional stability.
- Helps in deepening meditation and breath control.
- Improves flexibility in the hips, knees, and ankles.
- Enhances circulation in the lower body.
- Strengthens the back and core muscles.
3. Sitting Position – Vajrasana

Vajrasana, or the kneeling position, involves sitting back on your heels with knees bent and shins on the floor. The tops of the feet rest flat on the ground, and the spine is kept straight. This position is often used in traditional Japanese settings and for certain yoga postures.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Vajrasana is beneficial for digestive health and can be practiced after meals. It is also suitable for meditation, prayer, and some yoga poses. This position is ideal for those seeking to improve posture and increase flexibility in the legs and hips.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Aids in digestion when practiced after meals.
- Strengthens the thighs, knees, and ankles.
- Improves posture and spine alignment.
- Enhances concentration and focus.
- Can help relieve lower back pain.
4. Sitting Position – Seiza

Seiza involves sitting back on your heels with the tops of your feet flat on the floor and your knees bent. The spine is kept straight, and hands rest on the thighs. This traditional Japanese sitting position is often used in formal ceremonies and martial arts.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Seiza is suitable for formal occasions, meditation, and traditional Japanese tea ceremonies. It is also used in martial arts training. This position helps improve posture and discipline, though it may require practice to sit comfortably for extended periods.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Promotes good posture and spinal alignment.
- Strengthens the lower body, particularly the knees and thighs.
- Enhances mindfulness and discipline.
- Helps in digestion and alleviates bloating.
- Encourages calmness and mental clarity.
5. Sitting Position – Kursi Pe Baithna
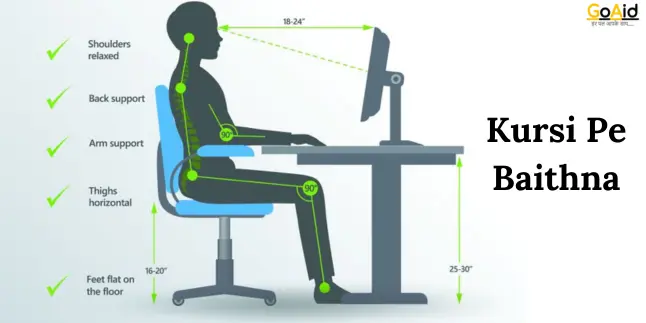
Chair sitting, or Kursi Pe Baithna involves sitting on a chair with your back straight, feet flat on the floor, and knees at a 90-degree angle. The spine is supported by the chair’s backrest, and arms can rest on armrests or the lap.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Chair sitting is ideal for office work, dining, and other activities requiring prolonged sitting. It is suitable for maintaining good posture and reducing strain on the back and legs. Ergonomically designed chairs enhance comfort and productivity in this position.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Provides back support and helps maintain good posture.
- Reduces strain on the lower body compared to floor sitting.
- Can be ergonomically adjusted to enhance comfort and productivity.
- Supports prolonged sitting with minimal discomfort.
- Suitable for various activities like working, dining, and studying.
Also Read: Top 10 Private Cancer Hospitals in Delhi
6. Sitting Position – Aram Se Baithna
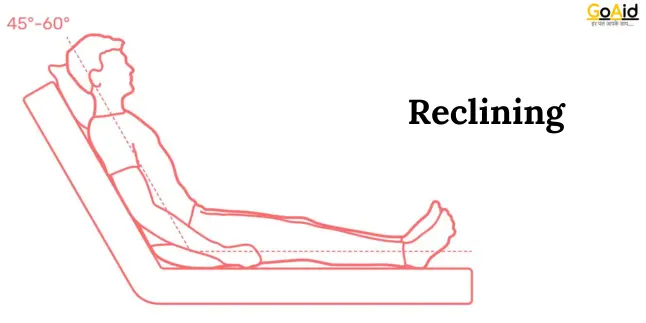
Reclining, or Aram Se Baithna, involves sitting with your back leaned back at an angle, supported by a chair or sofa, often with legs extended. This relaxed posture allows for comfortable lounging and resting, reducing tension in the spine and muscles.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Reclining is ideal for relaxation, reading, watching TV, or napping. It is suitable for times when you want to unwind and relieve stress. This position is also beneficial for those with back pain, as it provides support and reduces pressure on the spine.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Relieves pressure on the spine and reduces back pain.
- Promotes relaxation and stress relief.
- Helps in recovery from fatigue and enhances comfort.
- Can improve circulation when the legs are elevated.
- Supports restful activities like reading and watching TV.
7. Sitting Position – Malasana

Malasana, or the squatting position, involves sitting with knees bent and heels close to the buttocks, with feet flat on the ground. The back is kept straight, and hands can be placed together in a prayer position or on the knees. This position is common in many cultures for eating or resting.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Malasana is ideal for improving flexibility in the hips and ankles, and it aids in digestion. It is suitable for yoga practice, deep stretching, and as a resting position during outdoor activities. This position is also helpful for those seeking to strengthen their lower body.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Improves flexibility in the hips, ankles, and knees.
- Strengthens the lower body muscles.
- Aids in digestion and bowel movements.
- Enhances balance and stability.
- Can be used as a resting position during physical activities.
8. Sitting Position – Side Sitting – Ek Or Se Baithna

Ek Or Se Baithna, or side sitting, involves sitting with legs bent to one side, often with weight supported on one hip and one hand on the floor. The spine is slightly curved, and the other hand can rest on the lap or be used for support.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Side sitting is ideal for informal gatherings, floor activities, and light stretches. It is suitable for those who want to take a break from traditional sitting positions and engage different muscle groups. This position can be comfortable for short periods and helps in maintaining hip flexibility.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Provides a break from conventional sitting positions.
- Enhances flexibility in the hips and spine.
- Can improve lateral muscle strength.
- Encourages relaxation and a casual seating option.
- Suitable for informal settings and conversations.
9. Sitting Position – Baddha Konasana

Baddha Konasana, or the butterfly position, involves sitting with the soles of the feet together and knees bent outward. The back is kept straight, and hands can hold the feet or rest on the knees. This position promotes flexibility and is commonly used in yoga and stretching routines.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Baddha Konasana is ideal for stretching the inner thighs, hips, and groin. It is suitable for yoga practice, warm-up exercises, and cooling down after workouts. This position is beneficial for improving posture and relieving tension in the lower body.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Increases flexibility in the inner thighs, groin, and hips.
- Stimulates abdominal organs and improves digestion.
- Relieves tension in the lower back.
- Promotes relaxation and reduces stress.
- Enhances blood circulation in the pelvic region.
10. Sitting Position – Upavistha Konasana

Upavistha Konasana, or the straddle position, involves sitting with legs spread wide apart and back straight. The hands can rest on the floor or reach towards the feet. This position is used in yoga and stretching exercises to improve flexibility in the hamstrings and lower back.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Upavistha Konasana is ideal for deep stretching of the legs and spine. It is suitable for yoga practice, physical therapy, and as a preparatory pose for other advanced stretches. This position helps in increasing flexibility and reducing muscle stiffness.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Improves flexibility in the hamstrings, inner thighs, and lower back.
- Enhances posture and spinal alignment.
- Stretches the groin and hip flexors.
- Relieves tension and stiffness in the legs.
- Prepares the body for deeper yoga poses and stretches.
11. Sitting Position – Baddha Virasana

Baddha Virasana, or tailor sitting, involves sitting with knees bent and feet tucked under the thighs. The spine is kept straight, and hands can rest on the knees or lap. This comfortable position is often used in casual settings and for light stretches.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Baddha Virasana is ideal for informal gatherings, relaxation, and gentle stretching. It is suitable for those who want to maintain an upright posture while sitting on the floor. This position helps improve flexibility in the hips and knees and is often used in meditation.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Enhances flexibility in the hips and knees.
- Promotes good posture and an upright spine.
- Provides a comfortable sitting position for informal settings.
- Can be used for meditation and relaxation.
- Strengthens the lower body muscles.
Also Read: Introduction to Standard Protocols for Paramedics to Follow
12. Sitting Position – Paschimottanasana

Paschimottanasana, or forward bend, involves sitting with legs extended and bending forward from the hips, reaching towards the feet. The back is kept as straight as possible, and the hands can grasp the feet or shins. This position is commonly used in yoga and stretching routines.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Paschimottanasana is ideal for stretching the spine, hamstrings, and lower back. It is suitable for yoga practice, warm-up exercises, and as a relaxation pose. This position helps in relieving stress, improving flexibility, and enhancing circulation.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Stretches the spine, hamstrings, and lower back.
- Calms the mind and relieves stress.
- Improves digestion and stimulates abdominal organs.
- Enhances flexibility and range of motion.
- Helps in relieving menstrual discomfort and menopausal symptoms.
13. Sitting Position – W Baithna

W Baithna, or W-sitting, involves sitting with knees bent and legs splayed out to the sides, forming a W shape with the legs. The back is kept straight, and hands can rest on the knees or floor. This position is commonly seen in children.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
W-sitting is often used by children during play or activities on the floor. It is suitable for short periods but should be avoided for prolonged sitting as it may lead to hip and knee issues. This position can help in engaging different muscle groups but should be balanced with other sitting positions.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Engages different muscle groups in the lower body.
- Can provide stability and balance during play activities.
- Allows for active engagement and movement.
- Helps in maintaining an upright posture.
- Supports short-term sitting for children during activities.
14. Sitting Position – Parsva Upavistha Konasana

Parsva Upavistha Konasana, or side straddle, involves sitting with one leg extended to the side and the other bent. The back is kept straight, and hands can reach towards the extended foot or rest on the floor. This position is used in yoga and stretching exercises.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Parsva Upavistha Konasana is ideal for stretching the legs, hips, and spine. It is suitable for yoga practice, physical therapy, and warm-up exercises. This position helps increase flexibility and relieve tension in the lower body.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Stretches the legs, hips, and spine.
- Enhances flexibility and range of motion.
- Improves balance and coordination.
- Relieves tension in the lower body.
- Prepares the body for deeper stretches and yoga poses.
15. Sitting Position – Kinare Par Baithna

Kinare Par Baithna, or perching, involves sitting on the edge of a chair with thighs at a downward angle, often with feet flat on the floor. The spine is kept straight, and hands can rest on the knees or chair. This position maintains a semi-standing posture.
When should you sit in this type of sitting position?
Perching is ideal for tasks requiring frequent standing and sitting, such as working at a high desk or counter. It is suitable for maintaining good posture and reducing strain on the back and legs. This position helps promote active sitting and reduce fatigue.
Benefits of this type of Sitting Position
- Encourages an active sitting posture.
- Reduces strain on the lower back and legs.
- Enhances focus and productivity.
- Suitable for tasks requiring frequent standing and sitting.
- Promotes better circulation and reduces fatigue.
Benefits of the Right Sitting Position
These are the key benefits of the right Sitting Positions
- Improves Posture:
Maintaining a proper sitting position helps in aligning the spine correctly, which prevents slouching and hunching. This alignment supports the natural curves of the spine, reducing the risk of developing postural issues and chronic back pain.
- Reduces Back and Neck Pain:
Correct sitting posture distributes body weight evenly and reduces strain on the lower back and neck. This can alleviate discomfort and prevent the development of musculoskeletal problems over time, including conditions like herniated discs and tension headaches.
- Enhances Circulation:
Sitting properly with feet flat on the floor and avoiding crossing legs can improve blood circulation. This helps prevent conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT), varicose veins, and swelling in the legs and feet.
- Boosts Energy and Focus:
Good posture facilitates better breathing and oxygen flow, which can increase energy levels and improve concentration. Proper sitting can reduce fatigue and enhance overall productivity, particularly during long periods of desk work.
- Prevents Muscle Strain and Fatigue:
By supporting the bodyŌĆÖs natural alignment, a proper sitting position minimizes unnecessary muscle strain and fatigue. It ensures that muscles work efficiently without overexertion, reducing the risk of muscle tightness, spasms, and long-term injury.
- Supports Digestive Health:
Sitting upright can aid in digestion by preventing compression of the abdominal organs. This position can enhance gastrointestinal function and reduce the risk of issues like acid reflux and constipation, which are exacerbated by slouching.
- Promotes Better Breathing:
An erect posture opens up the chest cavity, allowing for deeper, more efficient breathing. This improved respiratory function can enhance overall well-being, reduce stress, and support cardiovascular health.
- Improves Confidence and Mood:
Good posture is often associated with confidence and assertiveness. Sitting upright can positively impact your mood and self-esteem, as the physical stance can influence psychological states, promoting a sense of well-being and reducing stress levels.
- Prevents Work-Related Injuries:
For those who work at a desk or computer, the right sitting position can prevent repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) like carpal tunnel syndrome. Proper ergonomics, including the use of adjustable chairs and proper desk height, can mitigate these risks.
- Enhances Physical Appearance:
Maintaining a good sitting posture can have aesthetic benefits. It helps in avoiding the development of a hunched back or rounded shoulders, contributing to a more upright and confident physical appearance.
BOOK AMBULANCE: GoAid Ambulance Service
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding different types of sitting positions is essential for maintaining good posture, enhancing flexibility, and promoting overall well-being. We have provided detailed information on various sitting positions, including when to use them and their specific benefits.
Additionally, the importance of the right sitting position cannot be overstated, as it prevents pain, improves circulation, and boosts energy levels. By incorporating these positions into your daily routine, you can achieve better health and comfort. If you have any questions or need further clarification, please feel free to ask in the comment box.
FAQs about Different Types of Sitting Positions
The most common types of sitting positions include cross-legged (Sukhasana), lotus position (Padmasana), kneeling (Vajrasana), chair sitting, and reclining. Each position serves different purposes, from meditation and yoga to everyday activities.
Different sitting positions offer various health benefits such as improved posture, reduced back and neck pain, enhanced circulation, better digestion, and increased flexibility. For example, cross-legged positions can promote relaxation and concentration, while kneeling positions aid in digestion and spine alignment.
Sitting positions like Sukhasana (cross-legged) and Padmasana (lotus position) are suitable for meditation due to their ability to promote relaxation, maintain a straight spine, and enhance focus. These positions encourage mindfulness and calmness during meditation practice.
Sitting on a chair provides back support, reduces strain on the lower back, and is suitable for prolonged sitting during work or study. On the other hand, sitting on the floor in cross-legged or kneeling positions improves flexibility, strengthens core muscles, and supports meditation and yoga practices.
Correct sitting positions, such as maintaining an upright spine and avoiding slouching, contribute to better posture and spine health. These positions reduce the risk of developing back pain, muscle tension, and spinal misalignment over time.
Certain sitting positions, like deep squats or W-sitting, should be avoided for prolonged periods as they may strain the knees, hips, or back. Individuals with specific musculoskeletal conditions should consult a healthcare professional before adopting certain sitting postures.
Yes, adopting ergonomic sitting positions, such as sitting upright with feet flat on the floor or using a supportive chair, can enhance productivity and concentration. These positions improve blood circulation, reduce fatigue, and support mental alertness.
Sitting positions that allow for a relaxed abdomen, like kneeling (Vajrasana) or butterfly position (Baddha Konasana), can aid digestion by reducing pressure on the stomach and promoting better bowel movements. These positions improve gastrointestinal function and reduce bloating.
Yes, sitting positions that maintain a neutral spine alignment, such as using lumbar support on a chair or sitting in a reclined position, can help alleviate back pain. Avoiding slouching and supporting the lower back is key in managing and preventing discomfort.
Incorporating different sitting positions into daily routines involves choosing positions based on the activity and duration of sitting. For example, using a chair for desk work, sitting on the floor for stretching exercises, and practicing meditation in cross-legged or lotus positions can diversify posture and support overall well-being.