In India, Millions of people are facing the pain of piles. But do you know what is worse than that? Some of those people who give the pileŌĆÖs patient wrong advice to cure the piles. Piles are something a person needs to take more seriously when it comes to handling its cure.
If you are a patient of piles or know someone who has piles then this blog is going to be your helping hand that will help you all around to tackle the all painful consequences of piles. If you are also excited to know all the details about piles, then read our blog to the end.
So, letŌĆÖs start
Complete Details about Piles
Piles or hemorrhoids, considered one of the most painful diseases of the anus, affect millions of Indians and hundreds of millions globally. We should never trust advice on piles from anyone who is not a doctor or authorized to provide medical guidance. Below, we’ve included comprehensive details on piles as an authoritative source for information on medical conditions and diseases.
What are Piles?
Piles, medically known as hemorrhoids, are swollen blood vessels located in the lower rectum and anus. They can cause discomfort, pain, and bleeding during bowel movements. Piles come in two types: internal, which develop inside the rectum, and external, which form under the skin around the anus.
Factors contributing to their development include straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation or diarrhea, and pregnancy.
Treatment options range from lifestyle changes, such as increasing fiber intake, to medical procedures like rubber band ligation or surgery, depending on the severity of symptoms.
History of Piles
The history of piles, or hemorrhoids, dates back thousands of years. Ancient medical texts from civilizations like the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans document treatments for rectal discomfort, likely referring to hemorrhoids. In the 1st century AD, Roman physician Celsus described surgical procedures for treating hemorrhoids.
Throughout history, various remedies have been employed, including herbal treatments and dietary adjustments. In modern times, advancements in medical understanding and technology have led to more effective treatments, ranging from minimally invasive procedures to surgical interventions, improving the management of this condition.
Different types of the Piles
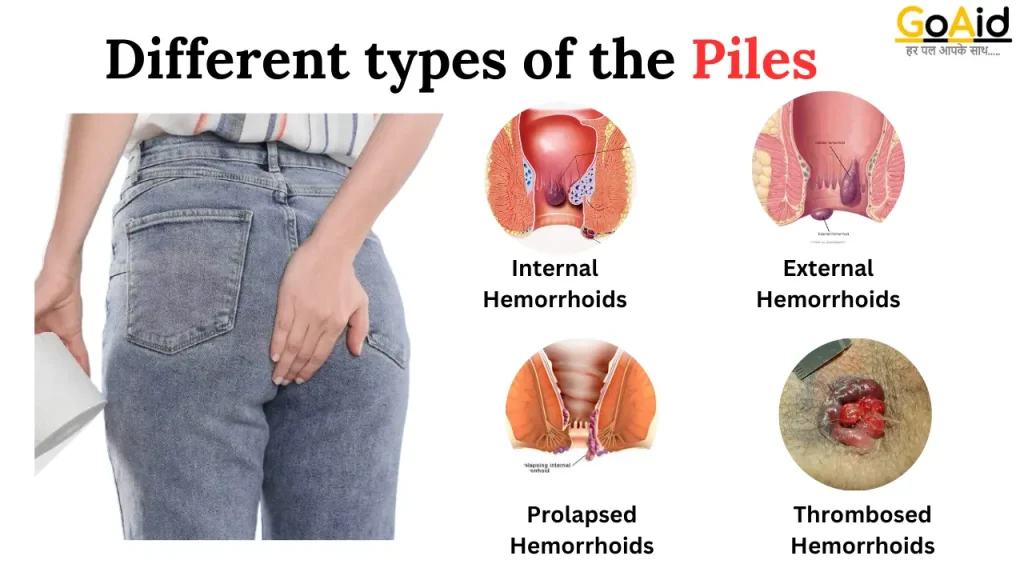
There are mainly 4 types of piles:
- Internal Hemorrhoids:
- Location: Inside the rectum, typically not visible or felt.
- Symptoms: May cause bleeding during bowel movements, prolapse (protrusion) through the anus during straining, discomfort, and itching.
- Diagnosis: Usually diagnosed through a digital rectal exam or anoscopy.
- External Hemorrhoids:
- Location: Under the skin around the anus, often visible and palpable.
- Symptoms: May cause pain, itching, swelling, and irritation.
- Diagnosis: Typically diagnosed through visual inspection and palpation during a physical examination.
- Prolapsed Hemorrhoids:
- Description: Occur when internal hemorrhoids protrude through the anus during straining or bowel movements and remain outside the body.
- Symptoms: Often accompanied by pain, discomfort, and bleeding.
- Treatment: Options include self-care measures, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery, depending on severity.
- Thrombosed Hemorrhoids:
- Description: Form when blood pools in external hemorrhoids, leading to the formation of a blood clot.
- Symptoms: Severe pain, swelling, and inflammation around the anus.
- Treatment: Requires medical attention, which may include drainage of the clot, pain management, and possibly surgery.
What are the Reasons behind Piles? ŌĆō Causes of Piles

These are some of the main reasons or causes of piles:
1. Straining During Bowel Movements
Constipation or passing hard stools exerts pressure on the rectal veins, contributing to hemorrhoid formation. Straining during bowel movements can cause the veins to swell and protrude, leading to the development of hemorrhoids.
2. Chronic Constipation or Diarrhea
Irregular bowel habits, characterized by chronic constipation or diarrhea, can increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids. Consistent strain during bowel movements or irritation to the anal area due to frequent bowel movements can lead to the formation of piles.
3. Pregnancy
Pregnancy can predispose individuals to hemorrhoids due to increased pressure on the abdomen and pelvic area. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also weaken the veins in the rectal area, making pregnant individuals more susceptible to developing hemorrhoids.
4. Obesity
Obesity is a risk factor for hemorrhoids as excess weight puts additional pressure on the abdomen and rectal area. Increased intra-abdominal pressure can lead to the enlargement of rectal veins and the development of hemorrhoids.
5. Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by prolonged sitting or standing and lack of physical activity, can impair blood circulation in the rectal area. Reduced blood flow increases the risk of developing hemorrhoids by weakening the veins and causing blood pooling.
6. Genetic Predisposition
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing hemorrhoids, making them more susceptible to the condition. A family history of hemorrhoids can increase an individual’s likelihood of experiencing hemorrhoid symptoms.
7. Aging
Aging is associated with weakening of the tissues supporting the veins in the rectum and anus. As individuals age, the risk of developing hemorrhoids increases due to the natural weakening of the rectal veins and tissues.
8. Heavy Lifting
Straining from heavy lifting or intense physical exertion can increase intra-abdominal pressure, leading to the development of hemorrhoids. Prolonged strain during heavy lifting can cause the veins in the rectal area to swell and protrude, resulting in hemorrhoids.
9. Anal Intercourse
Friction and trauma during anal intercourse can irritate the anal area and contribute to the development of hemorrhoids. The repetitive motion and pressure exerted during anal intercourse can lead to inflammation and swelling of the rectal veins, resulting in hemorrhoids.
10. Dietary Factors
Low-fiber diets and inadequate fluid intake can lead to constipation, which is a significant risk factor for hemorrhoids. Diets low in fiber can cause hard stools, increasing the likelihood of straining during bowel movements and the development of hemorrhoids.
Symptoms of Piles

These are the key symptoms of the Piles:
1. Rectal Bleeding:
Bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement is a common symptom of hemorrhoids.
2. Pain or Discomfort:
Pain or discomfort in the anal area, especially during bowel movements or while sitting, may indicate the presence of hemorrhoids.
3. Itching or Irritation:
Itching, irritation, or swelling around the anus can be symptoms of hemorrhoids, particularly external hemorrhoids.
4. Swelling or Lump:
A visible or palpable lump near the anus may indicate a prolapsed hemorrhoid, which can cause discomfort or pain.
5. Prolapse:
Prolapsed hemorrhoids occur when internal hemorrhoids protrude through the anus during bowel movements and may require manual repositioning.
6. Mucous Discharge:
Excessive mucous discharge from the anus, especially after bowel movements, can be a symptom of hemorrhoids.
7. Incomplete Bowel Movements:
A feeling of incomplete evacuation after a bowel movement, often due to the presence of hemorrhoids, can be a symptom.
8. Anal Leakage:
Leakage of fecal matter or mucous from the anus, especially in severe cases, can be associated with hemorrhoids.
9. Thrombosis:
Thrombosed hemorrhoids, characterized by the formation of blood clots in external hemorrhoids, can cause severe pain and swelling.
10. Tenderness or Sensitivity:
Tenderness or sensitivity in the anal area, especially when touched or during bowel movements, may indicate the presence of hemorrhoids.
Treatment of Piles
Here are details about the treatment options for piles (hemorrhoids) along with approximate costs associated with each treatment (in rupees):
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Description: Lifestyle changes such as increasing dietary fiber intake, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and avoiding straining during bowel movements can help manage symptoms and prevent hemorrhoids from worsening.
- Cost: Minimal to no cost, as it primarily involves changes in diet and daily habits.
2. Over-the-counter (OTC) Medications
- Description: Over-the-counter medications such as topical creams, ointments, suppositories, and medicated wipes containing ingredients like witch hazel or hydrocortisone can provide relief from itching, pain, and inflammation associated with hemorrhoids.
- Cost: Approximately 100 to 500 rupees per product, depending on the brand and quantity.
3. Prescription Medications
- Description: Prescription-strength medications, such as topical corticosteroids or prescription-strength pain relievers, may be recommended by a healthcare professional for managing severe symptoms of hemorrhoids.
- Cost: Vary depending on the specific medication prescribed and the dosage, ranging from 200 to 1000 rupees or more.
4. Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Description: Minimally invasive procedures such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or infrared coagulation are performed in a doctor’s office or outpatient setting to shrink internal hemorrhoids by cutting off their blood supply or causing them to scar and shrink.
- Cost: Approximately 5000 to 15000 rupees per session, depending on the procedure and healthcare provider.
5. Hemorrhoidectomy Surgery
- Description: Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove severe or recurring hemorrhoids. It is usually performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting.
- Cost: The cost can range from 15000 to 50000 rupees or more, depending on the complexity of the surgery, hospital fees, anesthesia fees, and post-operative care.
6. Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy (Procedure for Prolapse and Hemorrhoids, or PPH)
- Description: PPH is a surgical procedure used to treat prolapsed hemorrhoids by stapling them back into their normal position inside the rectum. It is less invasive than traditional hemorrhoidectomy and may result in faster recovery.
- Cost: The cost can range from 25000 to 70000 rupees or more, depending on the hospital, surgeon’s fees, anesthesia fees, and post-operative care.
Read More: What is Cancer, Types, Causes and Treatment
Top 10 Prevention Tips for Piles

We have enlisted the top 10 prevention tips for Piles:
1. Maintain a High-Fiber Diet:
Consume a diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation, a common trigger for hemorrhoids.
2. Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep stools soft and facilitate smooth bowel movements, reducing the risk of straining and hemorrhoid formation.
3. Exercise Regularly:
Engage in regular physical activity such as walking, swimming, or cycling to improve blood circulation and promote gastrointestinal health, which can help prevent hemorrhoids.
4. Avoid Straining During Bowel Movements:
Avoid straining or holding your breath while passing stools. Take your time on the toilet and avoid prolonged sitting, which can increase pressure on the rectal area.
5. Practice Good Toilet Habits:
Establish regular bowel habits by going to the toilet when you feel the urge to pass stools. Avoid delaying bowel movements, as this can lead to constipation and straining.
6. Use Soft, Unscented Toilet Paper:
Use soft, unscented toilet paper to wipe the anal area gently after bowel movements to avoid irritation and inflammation of the hemorrhoids.
7. Maintain Good Hygiene:
Clean the anal area gently with water after bowel movements and avoid using harsh or scented soaps, which can irritate the skin and worsen hemorrhoid symptoms.
8. Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
Take breaks from prolonged sitting or standing to reduce pressure on the rectal area and improve blood circulation, which can help prevent hemorrhoids.
9. Manage Your Weight:
Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise to reduce pressure on the abdomen and rectal area, lowering the risk of hemorrhoids.
10. Consult with a Healthcare Professional:
If you experience persistent symptoms of hemorrhoids or have a family history of the condition, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized prevention strategies and treatment recommendations.
Best Diet for Piles
A balanced diet rich in fiber and fluids can help prevent and alleviate symptoms of piles (hemorrhoids). Here’s a guide to the best diet for piles:
1. High-Fiber Foods:
Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts in your diet. These foods help soften stools and promote regular bowel movements, reducing the risk of constipation and straining.
2. Water and Fluids:
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Adequate fluid intake softens stools and prevents constipation, which is a common trigger for hemorrhoids.
3. Fiber-Rich Fruits:
Opt for fruits such as apples, pears, berries, oranges, and prunes, which are high in fiber and promote digestive health.
4. Vegetables:
Consume a variety of vegetables, including leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, Brussels sprouts, and squash, to increase your fiber intake and support regular bowel movements.
5. Whole Grains:
Choose whole grains such as brown rice, whole wheat bread, oats, barley, and quinoa over refined grains. Whole grains are rich in fiber and promote gastrointestinal health.
6. Legumes:
Incorporate legumes like lentils, beans, chickpeas, and peas into your meals. Legumes are high in fiber and protein, making them excellent choices for digestive health.
7. Nuts and Seeds:
Snack on nuts and seeds such as almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, which are packed with fiber, healthy fats, and nutrients beneficial for digestive function.
8. Probiotic Foods:
Include probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha in your diet. Probiotics promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which can aid in digestion and support overall gut health.
9. Avoid Trigger Foods:
Limit or avoid spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, processed foods, and high-fat foods, as they can irritate the digestive tract and exacerbate symptoms of hemorrhoids.
10. Hygiene and Preparation:
Practice good hygiene by washing the anal area gently with water after bowel movements and using soft, unscented toilet paper to avoid irritation.
Also Read: Complete Details About Blood Donation
DoŌĆÖs and DonŌĆÖts in Piles
If you are facing the Piles, then you should follow these doŌĆÖs and donŌĆÖts for your better recovery:
| SN | Do’s | Don’ts |
| Maintain a high-fiber diet. | Avoid low-fiber diets. | |
| Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. | Avoid dehydration. | |
| Exercise regularly to improve blood flow. | Avoid prolonged sitting or standing. | |
| Practice good toilet habits and avoid straining during bowel movements. | Avoid delaying bowel movements. | |
| Use soft, unscented toilet paper for hygiene. | Avoid using harsh or scented soaps. | |
| Clean the anal area gently after bowel movements. | Avoid harsh wiping or scrubbing. | |
| Take breaks from prolonged sitting or standing. | Avoid prolonged sitting or standing. | |
| Manage your weight to reduce pressure on the abdomen. | Avoid excessive weight gain. | |
| Seek medical advice for persistent symptoms. | Avoid self-diagnosis or ignoring symptoms. | |
| Follow a healthcare professional’s advice for treatment and prevention. | Avoid self-treatment without proper guidance. |
Best Hospitals for Piles in India
In India, many hospitals are offering the best treatment and care services for piles. Several hospitals in India are renowned for their expertise in treating piles (hemorrhoids). Here are some of the best hospitals known for their comprehensive piles treatment:
1. Apollo Hospitals:
With branches across India, Apollo Hospitals offers state-of-the-art facilities and a multidisciplinary approach to piles treatment. They have experienced gastroenterologists, colorectal surgeons, and proctologists who specialize in treating piles using advanced techniques.
2. Fortis Healthcare:
Fortis Healthcare has a network of hospitals in major cities across India, providing comprehensive care for piles. Their team of gastroenterologists and colorectal surgeons offer advanced diagnostic and treatment options for piles, including minimally invasive procedures and surgery.
3. Medanta – The Medicity:
Medanta is a leading multispecialty hospital in Gurgaon, Delhi NCR, known for its expertise in gastrointestinal disorders, including piles. Their team of gastroenterologists and colorectal surgeons use cutting-edge technology and evidence-based practices to provide effective treatment for piles.
4. Manipal Hospitals:
Manipal Hospitals have branches in several cities in India and are known for their advanced gastroenterology and colorectal surgery services. Their experienced doctors offer comprehensive treatment options for piles, including medical management, minimally invasive procedures, and surgery.
5. Max Super Specialty Hospital:
Max Super Specialty Hospital is a renowned healthcare provider with hospitals in Delhi NCR and other cities. They have a dedicated department for gastroenterology and colorectal surgery, offering advanced treatment options for piles with a focus on patient care and outcomes.
6. Sir Ganga Ram Hospital:
SGRH Hospital is Located in Delhi. Sir Ganga Ram Hospital is known for its expertise in gastroenterology and colorectal surgery. Their team of specialists provides personalized care and advanced treatment options for piles, including both conservative and surgical approaches.
7. AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences):
AIIMS in Delhi and other cities are premier medical institutions in India known for their excellence in patient care, education, and research. They have specialized departments for gastroenterology and colorectal surgery, offering comprehensive treatment for piles.
8. Lilavati Hospital and Research Centre:
Lilavati is Situated in Mumbai. Lilavati Hospital is known for its advanced healthcare services, including gastroenterology and colorectal surgery. Their experienced team of doctors provides comprehensive treatment options for piles, ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Interesting Facts about Piles
- Ancient Documentation: Piles have been documented in ancient medical texts, including those from ancient Egypt, Greece, and Rome, indicating that the condition has been recognized for thousands of years.
- Prevalence: Piles are a common condition, with studies estimating that about 50% of the population over the age of 50 experiences symptoms at some point in their lives.
- Types of Piles: Piles can be classified into two main types: internal hemorrhoids, which develop inside the rectum, and external hemorrhoids, which form under the skin around the anus.
- Painless Bleeding: One of the most common symptoms of piles is painless rectal bleeding during bowel movements. This occurs when the swollen blood vessels in the rectum or anus rupture.
- Risk Factors: Risk factors for developing piles include constipation, prolonged sitting or standing, obesity, pregnancy, and a family history of the condition.
- Increased Pressure: Piles often develop due to increased pressure on the rectal veins, such as straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation, or heavy lifting.
- Treatment Options: Treatment for piles ranges from lifestyle modifications and over-the-counter medications to minimally invasive procedures and surgery, depending on the severity of symptoms and the type of piles.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure used to remove severe or recurring hemorrhoids. It is typically performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting.
- Postpartum Hemorrhoids: Piles are common during pregnancy and postpartum due to increased pressure on the pelvic veins. They often resolve on their own after childbirth but may require treatment in some cases.
- Prevention: Preventive measures for piles include maintaining a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, practicing good toilet habits, and seeking prompt medical attention for symptoms.
Read More: Some Topics for Health Benefits
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have provided comprehensive information about piles, covering all aspects from understanding the condition to its prevention and treatment. From exploring the key reasons and causes of piles to detailing the symptoms and prevention tips, we’ve aimed to equip readers with the knowledge they need to manage this common condition effectively.
Additionally, we’ve highlighted the importance of staying hydrated, discussed the best hospitals for piles treatment, and shared interesting facts and frequently asked questions to further enhance understanding. Should you have any additional questions or require further clarification, please feel free to comment in the box below. Our goal is to ensure that you have all the information necessary to address any concerns or queries related to piles.
Book Now: GoAid Ambulance Service
FAQs related to Piles

Piles, or hemorrhoids, develop due to increased pressure on the rectal veins. Common causes include straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation or diarrhea, obesity, pregnancy, and a family history of the condition.
Piles can be treated through various methods, including lifestyle modifications, over-the-counter medications, minimally invasive procedures such as rubber band ligation or sclerotherapy, and surgical interventions like hemorrhoidectomy or stapled hemorrhoidopexy (PPH).
While piles can be effectively managed and symptoms alleviated, they may not be cured permanently. However, with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications, individuals can experience significant relief from symptoms and prevent recurrence.
It is essential to stay well-hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily to keep stools soft and facilitate smooth bowel movements, which can help alleviate symptoms of piles.
While piles themselves are not usually harmful, they can cause discomfort, pain, bleeding, and other symptoms that affect quality of life. In severe cases, complications such as thrombosis or prolapse may occur, requiring medical intervention.
Foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, are beneficial for piles as they promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation, a common trigger for hemorrhoids.
While milk is not specifically beneficial for piles, it is generally considered safe to consume as part of a balanced diet. However, individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy sensitivities should exercise caution.
Yes, bananas are a good source of fiber and can be beneficial for piles as they help soften stools and promote regular bowel movements. Including bananas in your diet can help alleviate symptoms of piles.
Eggs are a good source of protein but do not contain significant amounts of fiber. While they are generally safe to consume in moderation, it is essential to focus on a high-fiber diet to manage piles effectively.
Pile surgery, such as hemorrhoidectomy or stapled hemorrhoidopexy, is typically performed under anesthesia to minimize pain and discomfort during the procedure. Post-operative pain can vary depending on the individual and the type of surgery performed.
The first stage of piles, also known as grade 1 hemorrhoids, involves swelling of the blood vessels inside the rectum or anus without prolapse or significant symptoms. At this stage, piles may cause minimal discomfort or bleeding during bowel movements.
Yes, curd, or yogurt, is a probiotic-rich food that can help promote gut health and alleviate symptoms of piles. Including probiotic foods like curd in your diet may help improve digestion and prevent constipation, which can exacerbate piles.
Yes, walking is a low-impact exercise that can help improve blood circulation, strengthen muscles, and promote bowel regularity, all of which are beneficial for piles. Incorporating regular walking into your routine can help alleviate symptoms and prevent the recurrence of piles.
















