In India, people are merely aware of the treatment of Diabetes, so being aware of types of Diabetes is a very rare thing to expect. To fight with Diabetes, we need to know which kind of Diabetes we are fighting with. There are several types of Diabetes about we must know of.
This is why, in this blog, we have added all the information about the type of Diabetes. If you are also willing to be aware of Types of Diabetes, then read this blog to the end. After reading it, youŌĆÖll be way ahead of many people who have no Idea of Diabetes.
So, letŌĆÖs start-
Why knowing of Types of Diabetes is Important?
Understanding the types of diabetes is important for personalized healthcare and effective disease management. Each type, whether it is Type 1, Type 2, gestational, or other rare forms, presents distinct challenges and requires tailored approaches to treatment.
Accurate diagnosis ensures individuals receive the most suitable interventions, from insulin therapy for Type 1 to lifestyle modifications for Type 2. Moreover, awareness of the types fosters early detection, enabling timely interventions that can mitigate complications.
By appreciating the nuances of each type, healthcare providers and individuals alike can collaborate in crafting targeted strategies, empowering better control and improved quality of life.
What are the Types of Diabetes?
We consider mainly 5 types of Diabetes. We have listed brief information about all these types including their causes, and prevention & about these types below:
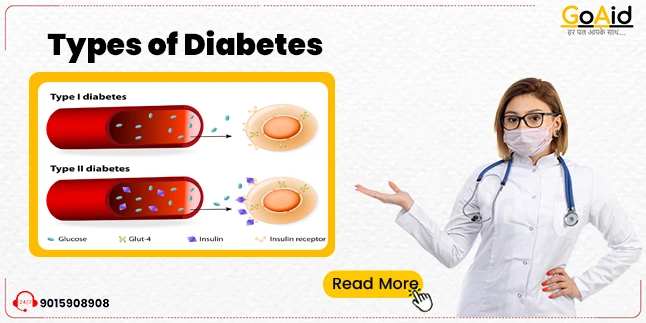
Type 1 Diabetes
- About the Type: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to a lack of insulin production.
- Causes: Primarily genetic, with environmental factors possibly triggering the autoimmune response.
- What to Do: Requires lifelong insulin therapy, often through injections or an insulin pump. Regular blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, and exercise are essential components of management.
Type 2 Diabetes
- About the Type: Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where cells don’t respond effectively to insulin. Over time, the pancreas may produce less insulin.
- Causes: Mainly linked to lifestyle factors, including poor diet, sedentary behavior, and genetics.
- What to Do: Managed through lifestyle changes, oral medications, injectable medications, and, in some cases, insulin. Focus on weight management, healthy eating, and regular physical activity.
Gestational Diabetes
- About the Type: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Causes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy may contribute to insulin resistance.
- What to Do: Controlled through diet, exercise, and, in some cases, medication. Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial. After delivery, blood sugar levels typically return to normal, but there’s an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes.
LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults)
- About the Type: LADA is a form of autoimmune diabetes that appears in adulthood, initially resembling Type 2 diabetes but progressing more like Type 1.
- Causes: An autoimmune response leading to the gradual loss of insulin-producing cells.
- What to Do: Treatment may start with oral medications but often progresses to insulin therapy. Regular monitoring and a proactive approach to management are essential.
Monogenic Diabetes
- About the Type: Monogenic diabetes is a rare form caused by a single gene mutation affecting insulin production.
- Causes: Genetic mutations inherited from one or both parents.
- What to Do: Treatment varies based on the specific genetic defect. Medications or insulin therapy may be prescribed, and management is tailored to the genetic cause.
Also Read: Book Ambulance Service from Mumbai to Bihar
Symptoms of all types
There are some precise symptoms of all these types of Diabetes. We have listed some common & precise symptoms of all these 5 types of Diabetes below:
1. Type 1 Diabetes
- Frequent Urination: Excessive urination, known as polyuria, can be a sign of elevated blood sugar levels.
- Excessive Thirst: Increased fluid loss through urination leads to persistent thirst.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite normal or increased food intake, individuals may experience rapid weight loss.
- Extreme Fatigue: Insufficient glucose uptake by cells can result in persistent fatigue.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can cause changes in the shape of the eye lens, affecting vision.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
- Increased Thirst and Hunger: Elevated blood sugar levels trigger increased thirst and hunger.
- Frequent Urination: Excess glucose in the blood prompts the kidneys to work harder, leading to increased urination.
- Fatigue: Cells may not receive sufficient energy due to insulin resistance.
- Blurred Vision: Similar to Type 1, high blood sugar levels can impact vision.
- Slow Wound Healing: Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal.
3. Gestational Diabetes
- Increased Thirst and Hunger: Similar symptoms to Type 2 diabetes may manifest during pregnancy.
- Frequent Urination: Excess glucose in the blood prompts increased urination.
- Fatigue: Due to changes in metabolism during pregnancy.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can affect vision temporarily.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Some women may experience these symptoms.
4. LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults)
- Gradual Onset of Symptoms: Symptoms may develop slowly over time.
- Increased Thirst and Urination: Similar to Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- Fatigue: Due to the body’s inability to use glucose for energy.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite normal or increased food intake.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels impacting the eyes.
5. Monogenic Diabetes
- Neonatal Diabetes Symptoms: If diagnosed in infancy, symptoms may include dehydration, frequent urination, and failure to thrive.
- Unexplained Hypoglycemia: Some forms of monogenic diabetes may present with low blood sugar levels.
- Developmental Delays: In cases of neonatal diabetes, developmental delays may be observed.
- Family History: A significant number of cases have a family history of diabetes.
- Distinct Clinical Features: Each subtype of monogenic diabetes may have unique clinical characteristics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the diverse types of diabetes and their distinct symptoms is paramount for early detection and tailored management. Recognizing the nuances enables timely interventions, empowering individuals to navigate their diabetes journey with precision.
Whether it’s the autoimmune nature of Type 1, the lifestyle influence on Type 2, or the unique characteristics of gestational, LADA, and monogenic diabetes, personalized care is key. Awareness cultivates proactive health choices, fostering a future where diabetes is effectively controlled and its impact minimized.